Greenhouse Gases
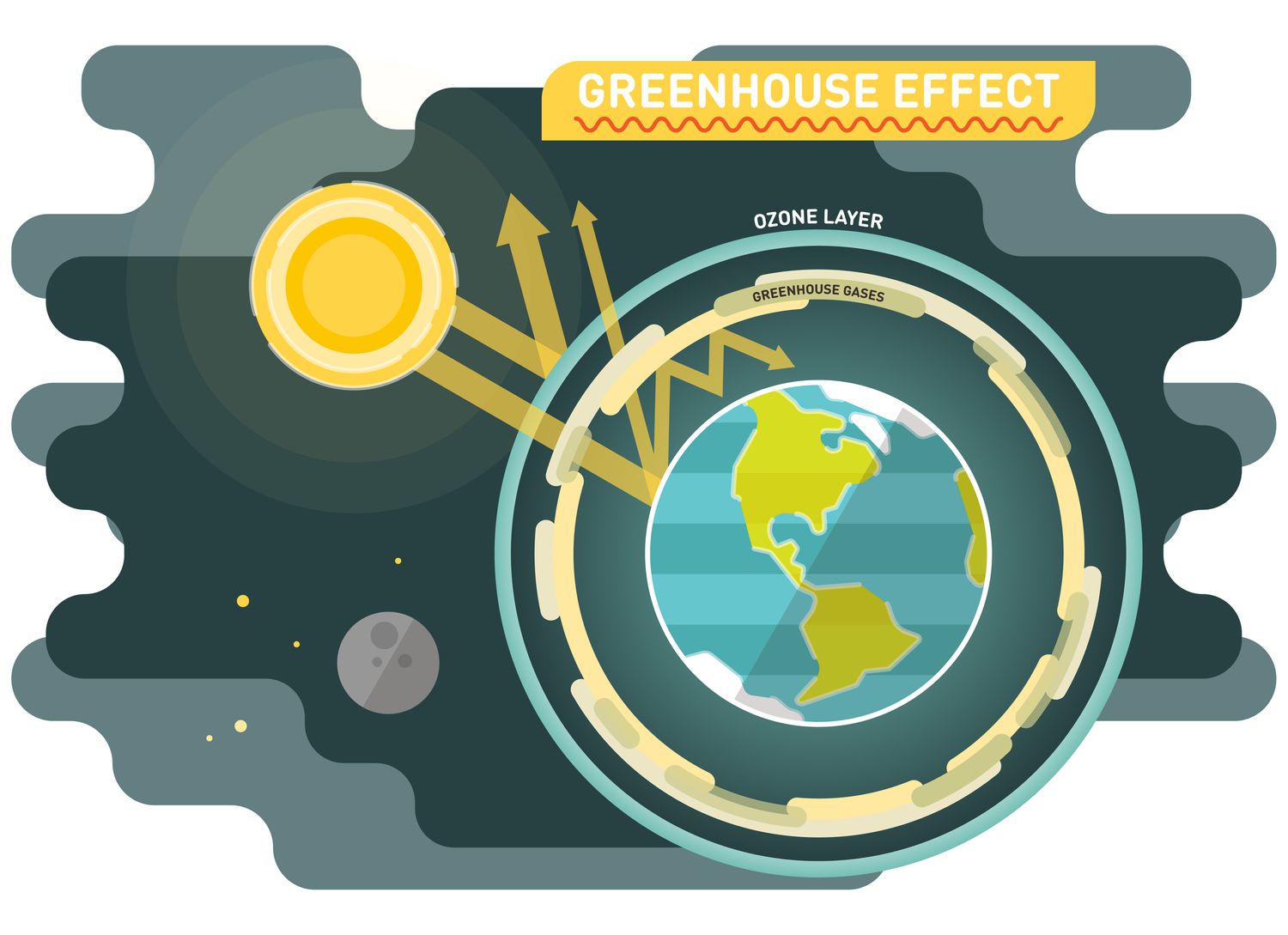
Greenhouse gases are essential components of Earth's atmosphere, trapping heat and maintaining a temperature suitable for life. However, human activities have significantly altered the balance, resulting in a range of environmental consequences.
Greenhouse gases, both natural and human-made, include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), water vapor, and fluorinated gases. While water vapor is abundant, human activities contribute significantly to increased concentrations of CO2, CH4, and N2O.
Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and certain agricultural practices, release large amounts of these gases into the atmosphere. The consequences of elevated greenhouse gas levels are far-reaching and impact various aspects of our environment.
Global warming, a direct result of the enhanced greenhouse effect, leads to climate change. This warming is associated with more frequent and severe weather events, including hurricanes, droughts, and heatwaves. Melting ice caps and rising sea levels threaten coastal areas and low-lying islands.
Ocean acidification, caused by the absorption of excess CO2 by the oceans, harms marine life and disrupts ecosystems. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns further contribute to the disruption of plant and animal life.
Addressing the consequences of increased greenhouse gas levels requires concerted efforts and sustainable practices. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, afforestation, reforestation, and improving energy efficiency are essential steps toward mitigating the impact of human activities on our planet. It is a collective responsibility to work towards a more environmentally friendly future.

